Bölüm Başkanı
Karabük Üniversitesi, Yazılım Mühendisliği

Dr. Caner ÖZCAN, Karabük ili doğumlu olup; ilk, orta ve lise öğrenimini bu şehirde tamamlamıştır. 2008 yılında Yıldız Teknik Üniversitesi Bilgisayar Mühendisliği Bölümü'nden mezun oldu. 2015 yılında doktora çalışmalarını tamamlayarak mezun oldu ve 2016 yılı Ocak ayında Karabük Üniversitesi Bilgisayar Mühendisliği Bölümü'nde öğretim üyesi olarak göreve başladı. 2017 yılında Tübitak desteğiyle 10 ay süreyle ABD'de bulunan Purdue Üniversitesi'nde misafir öğretim üyesi olarak çalışmalarda bulundu. 2020 yılında TÜBİTAK BİGG Girişimci desteğini alarak Karabük Üniversitesi teknokentinde SimurgAI isimli yapay zeka şirketini kurmuştur. 2023 yılında 10 ay süreyle Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projeleri Koordinasyon Birimi Koordinatörlüğü görevini yürütmüştür.
2024 Temmuz ayından sonra Tübitak desteğiyle 12 ay süreyle ABD'de bulunan Kentucky Üniversitesi'nde misafir öğretim üyesi olarak sağlık alanında yapay zeka konusunda araştırmalar yapmıştır. Başlıca çalışma alanları arasında görüntü işleme, makine öğrenmesi, derin öğrenme ve uzaktan algılama yer almaktadır. Jestech dergisinde alan editörlüğü ve birçok alan dergisinde ve projelerde hakemlik görevinde bulunmaktadır. Deneyap Teknoloji Atölyeleri kapsamında Yazılım Teknolojileri ders içeriklerini ve kitaplarını ortaokul ve lise öğrencileri için hazırlamıştır. Yazılım, görüntü işleme ve yapay zeka alanlarında çeşitli projeler yürütmekte ve kurumlara danışmanlık hizmeti vermektedir. Halen Karabük Üniversitesi Yazılım Mühendisliği Bölümü'nde Öğretim Üyesi ve Bölüm Başkanı olarak görevine devam etmektedir.
Karabük Üniversitesi, Yazılım Mühendisliği
Kentucky Üniversitesi, Biyomedikal Bilişim Enstitüsü
Karabük Üniversitesi, Yazılım Mühendisliği
Karabük Üniversitesi, Yazılım Mühendisliği
Karabük Üniversitesi, Bilgisayar Mühendisliği
Purdue Üniversitesi, Elektrik ve Bilgisayar Mühendisliği, Indiana, ABD
Karabük Üniversitesi, Bilgisayar Mühendisliği
Bilgisayar Mühendisliği ABD
Karabük Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü
Bilgisayar Mühendisliği ABD
Karabük Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü
Bilgisayar Mühendisliği Bölümü
Yıldız Teknik Üniversitesi, Elektrik Elektronik Fakültesi
Spor Yöneticiliği Bölümü
Karabük Üniversitesi, Hasan Doğan BESYO
Antrenörlük Eğitimi Bölümü
Karabük Üniversitesi, Hasan Doğan BESYO
Lisansüstü Tez Danışmanlıkları

* Semih GENÇAY, SAR, optik ve spektral uydu görüntülerinin füzyonunda gürültü giderme, kanal seçimi ve sınıflandırma başarısının değerlendirilmesi, Doktora, 2025
* Ayhan AYDIN, Derin Öğrenme Yaklaşımları Kullanılarak Kemik Dokusu Üzerindeki Enkondromun Tespiti Ve Segmentasyonu, Doktora, 2024
* Dilara ÖZDEMİR, Panoramik radyografi görüntüleri üzerinde diş çürüğünün derin öğrenme tabanlı yöntemler ile analizi ve tespiti, Yüksek Lisans, 2023
...
Daha fazla tez için tıklayınız...
* Elif MEŞECİ, Arazi örtüsü ve kullanımı için SAR görüntülerinin sınıflandırılmasında topluluk öğrenme tabanlı yaklaşım, Yüksek Lisans, 2023
* Süheda AKDAĞ, Spor bilimlerinde kullanılan Y-Denge verilerinin makine öğrenimi yöntemleri ile analizi, Yüksek Lisans, 2023
* Ahmet KARAOĞLU, Diş Yapısının ve Özelliklerinin Belirlenmesinde Panoramik Radyografi Görüntülerinin Yapay Öğrenme Yöntemleri ile Analizi, Doktora, 2023
* Merve ÖZKAN, Masif Panel Üretiminde Kullanılan Lamel Parçaları Üzerinde Nesne Tespiti ve Sınıflandırılması, Yüksek Lisans, 2023
* Hüseyin ÇİZMECİ, Derin Sinir Ağları İle EEG ve Alın EOG Tabanlı Duygu Analizi, Doktora, 2022
* Mehmet Zahid YILDIRM, Geliştirilmiş Katmanlı Uzay Yerleştirme Yöntemleri Kullanılarak Hiperspektral Görüntülerin Sınıflandırılması ve Görselleştirilmesi, Doktora, 2021
* Muhammed Çağrı ÇELİK, Atlas Vertebra Görüntülerinin Görüntü İşleme ile Otomatik Morfolojik Ölçümü ve Makine Öğrenmesi Cinsiyet Tahmini Modeli, Yüksek Lisans, 2021
* Buse Yaren TEKİN, Bitewing Ağiz İçi Radyografik Görüntülerde Derin Öğrenme ile Diş Segmentasyonu , Yüksek Lisans, 2021
* Cahit Berkay KAZANGİRLER, Elle Çizilmiş Taslak Çizimlerde Kullanıcı Arabirimi Ögelerinin Derin Örnek Segmentasyonu, Yüksek Lisans, 2021
* Ertan Yavuz KÖPRÜ, Yapay Sinir Ağları ile Sıvı Ham Demir Tahmini ve 5. Yüksek Fırın Uygulaması, Yüksek Lisans, 2020
* Betül DOLAPCI, Apache Spark Kullanılarak Büyük Boyutlu Görüntülerin Analizi, Yüksek Lisans, 2020
* Yasin ÖZTÜRK, NURBS Eğrilerinin FPGA Destekli Dokunmatik Ekranda Gerçekleştirilmesi, Yüksek Lisans, 2018
* Yadigar ERDEM, Büyük Verinin Makine Öğrenmesi Yöntemleri ile Apache Spark Teknolojisi Kullanılarak Sınıflandırılması, Yüksek Lisans, 2017
* İsmail Burak AKINCI, Gerçek Zamanlı Olarak Meyveleri Görüntü İşleme İle Sınıflandıran Otomasyon Sistemi, Yüksek Lisans, 2017

"Diş Hekimliğinde Kullanılan Panoramik Radyografilerdeki Hastalıkların Erken Teşhisi ve Tedavisi İçin Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Yazılım Geliştirilmesi", Proje No: 33480, Yürütücü
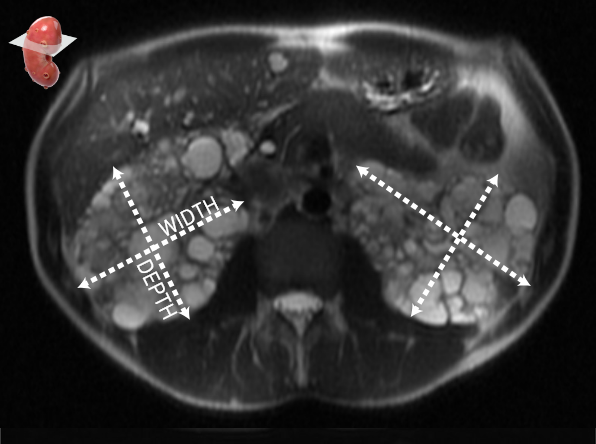
"Otozomal Dominant Polikistik Böbrek Hastalığı Manyetik Rezonans Görüntüleme Tabanlı Yapay Zekâ Karar Destek Sistemi: Prognoz Tahmini ve Tedavi Seçimi Ön Çalışması", Proje No: 33865, Araştırmacı
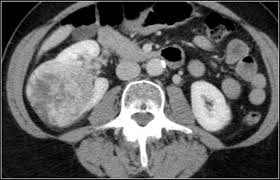
"İnsidental Böbrek Kanseri Tarama ve Tanısında Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Yapay Zeka Yazılımı", Proje No: 33756, Araştırmacı

"Öğretmen Adaylarının Yapay Zeka Okuryazarlığını Geliştirmeye Yönelik MOOC’un Tasarlanması ve Etkililiğinin Araştırılması", Proje No: -, Araştırmacı

"Derin Öğrenme Yaklaşımları Kullanılarak Kemik Dokusu Üzerindeki Kanserin Tespiti Ve Sınıflandırılması", Proje No: 122E636, Yürütücü

"Diş Hekimliğinde Elde Edilen Görüntülerin Yapay Zeka Destekli Otomatik Analizi (Dentiassist)", Proje No: 2200272, Yürütücü
Proje çıktısı, diş hekimliğindeki bu sorunları çözmek için tasarlanan cihaz, marka ve model bağımsız yapay zeka destekli bir analiz yazılımıdır. Diş hekimlerinin iş yükü azaltılarak daha verimli çalışmaları ve hastaların mevcut ağız durumlarının kolayca raporlanıp kaydedilerek, ağız sağlığının zaman içindeki değişiminin incelenebilmesi sağlanacaktır. Arşivdeki panoramik görüntülerin analiz edilebildiği bir arayüz yazılımı oluşturulacak, yapay zeka modeli ile eklenen yeni görüntülerin otomatik analizi sağlanacaktır. Yapay zekâ modülü, düşük maliyetli olması, veri güvenliği, farklı çözümlere uygun alt yapısı ve çoklu platformlarda (bilgisayar, tablet, akıllı telefon vb.) çalışabilme özelliği ürünümüzün özgün ve yenilikçi yönlerini oluşturacaktır. Böylelikle, Türkiye'de ilk kez hasta bazlı zamansal değişim analizi özelliği bulunan bir tespit sistemi oluşturulacaktır. Bu özellik sayesinde diş hekimleri tanı ve tedavi sürecini daha verimli bir şekilde yönetebileceklerdir.
Diş hekimliği uygulamalarının yapıldığı fakülteler, klinikler, poliklinikler, hastaneler; dental görüntüleme cihaz üreticileri ve sigorta şirketleri projenin hedef kitlelerini oluşturmaktadır. Geliştireceğimiz ürün sayesinde, tek bir platform üzerinden birden fazla analiz ve raporlama yapılarak hedef kitlelerimizin performanslarını arttırmayı planlamaktayız. Aynı zamanda, özellikle COVİD-19 gibi salgın sürecinde, enfeksiyonların en fazla bulaşma yeri olan hastanelerde: acil hastaların tespiti ve analizlerin hızlı yapılabilmesi sonucu hasta ile teması en aza indirerek tedavi opsiyonlarının belirlenmesi gibi konularda diş hekimlerine yardımcı olacaktır. Proje çıktısı ürünü, ülkemiz için ihracat potansiyeli yüksek olan Orta Doğu ve Avrupa pazarlarına sunarak hem diş sağlığı hem de sigortacılık sektörü üzerinden pazarımızı büyütmeyi planlıyoruz.

"Parçacık Sürü Optimizasyonu Tabanlı Katmanlı Uzay Yerleştirme Yöntemi Kullanılarak Hiperspektral Görüntülerin Sınıflandırılması Ve Görselleştirilmesi", Proje No: 120E404, Yürütücü
Birçok gerçek dünya nesnesi, görüntüler, konuşma sinyalleri, videolar ve metin belgeleri gibi yüksek boyutlu gösterimlerle ilişkilendirilebilir. Bu büyük veri setlerini analiz etmek ve işlemek, araştırmacılar için önemli bir çalışma alanıdır. Büyük veri kümeleri, karakter özelliklerini koruyarak daha küçük kümelere dönüştürülmelidir. Günümüzde gittikçe önem kazanan uzaktan algılamada, araştırmacılar çeşitli spektral imzalar arasındaki ilişkileri bulmak için dünyanın yüzeyini temsil eden yüksek boyutlu verileri kullanırlar. Özellikle görüntüler, farklı malzemelerin özelliklerini yansıtan yüzlerce yüksek çözünürlüklü banttan oluşur. Bununla birlikte, yüksek boyutlu uzayda çok sayıda farklı bantların bulunması, bu özelliklerin yorumlanmasını zorlaştırmaktadır. Uzaktan algılama verilerinin ön-işlemesi için boyutsallık problemine bağlı olarak çeşitli zorluklar ile karşılaşılmaktadır. Bu alanda uzun yıllardır ortaya çıkan araştırma, bunun zor bir problem olduğunu ve tüm sorunlara tek bir çözüm olmadığını ortaya koymaktadır. Bununla birlikte, son çalışmalar, hiperspektral görüntülerin ön işlemesinde boyut indirgeme ve katmanlı uzay öğrenme (manifold learning) tekniklerinin çok önemli bir çözüm olduğunu göstermektedir. Bu teknikler, görüntülerde daha iyi sıkıştırma ve görselleştirme olanağı sunarken, yararlı sınıflandırma özelliklerinin çıkarılmasını başarılı bir şekilde sağlar.
DBu projenin özgün değeri, kuvvet alan formülasyonuna dayanan çok boyutlu bir alan yerleştirme algoritması kullanarak hiperspektral görüntüleri yüksek doğruluk oranı ile mümkün olduğunca kısa sürede sınıflandırmak ve görselleştirmektir. Literatürdeki çalışmalar incelendiğinde kullanılan veri setlerinin boyutlarının çok büyük olması sebebiyle belirli oranlarda örneklenmiş parçaları üzerinde sınıflandırmalar yapıldığı görülmektedir. Çalışmamızda bu verilerin tümünü kullanarak daha yüksek doğruluk oranları elde etmeyi ve proje kapsamında talep edilen donanımlar ile bu işlemleri özellikle gerçek zamanlı uygulamalarda kabul edilebilir sürelerde gerçekleştirmeyi amaçlamaktayız. Ayrıca kullanılan yöntem için parçacık sürü optimizasyonu (PSO) temelli bir yaklaşımla, yöntem içerisindeki parametrelerin optimizasyonu sağlanacak ve bu yaklaşım ile çalışma zamanı ve sınıflandırma başarısının artırılması sağlanacaktır.

∴ Öz-Denetimli Öğrenme ile Servikal Kanser Teşhisinde Yeni Yaklaşımlar, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-25-YL-098, Haziran 2025 -
∴ SAR ve Optik Görüntüler Kullanılarak Görüntü Füzyonu İçin Hibrit Bir Yöntem Geliştirilmesi, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-23-KP-032, Mart 2023 - Mart 2025
∴ Makine Öğrenmesi Yöntemleri Kullanarak Yoğun Bakım Ünitesinde Yatan Hastaların Basınç Yaralanması Riskinin Tahmini, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Araştırmacı, Proje No: KBÜBAP-23-KP-068, Mayıs 2023 -
∴ Panoramik Radyografi Görüntüleri Üzerinde Diş Çürüğünün Derin Öğrenme Tabanlı Yöntemler ile Analizi ve Tespiti, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-23-YL-066, Mayıs 2023 - Ekim 2023
∴ Spor Bilimlerinde Kullanılan Y-denge Verilerinin Makine Öğrenimi Yöntemleri ile Analizi, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-23-YL-040, Mart 2023 - Ekim 2023
∴ Arazi Örtüsü ve Kullanımı için Sar Görüntülerinin Sınıflandırılmasında Topluluk Öğrenme Tabanlı Yaklaşım, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-23-YL-027, Mart 2023 - Ekim 2023
∴ Masif Panel Üretiminde Kullanılan Ağaç Malzemelerin Derin Öğrenme Yöntemiyle Gerçek Zamanlı Sınıflandırılması, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-22-YL-096, Temmuz 2022 - Şubat 2023
∴ Derin Sinir Ağları ile EEG ve Alın EOG Tabanlı Duygu Analizi, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: FDK-2020-2309, Temmuz 2020 - Ağustos 2022
∴ Hiperspektral Görüntülerin Boyut İndirgeme Yöntemleri ile İşlenmesi, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: FDT-2020-2315, Temmuz 2020 - Kasım 2021
∴ Elle Çizilmiş Taslak Çizimlerde Kullanıcı Arabirimi Ögelerinin Derin Örnek Segmentasyonu, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: FYL-2020-2156, Nisan 2020 - Kasım 2021
∴ Apache Spark Kullanılarak Büyük Boyutlu Görüntülerin Analizi, Karabük Üniversitesi Bilimsel Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: FYL-2019-2044, Mart 2019 - Eylül 2020
∴ Büyük Verinin Makine Öğrenmesi Yöntemleri ile Apache Spark Teknolojisi Kullanılarak Sınıflandırılması, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-17-YL-072, Ocak 2017 - Kasım 2017
∴ Bu projeler kapsamında çeşitli tez çalışmaları gerçekleştirilerek akademik yayınlar üretilmiştir.

"Görüntüler Üzerindeki Gürültüyü Gidermede Hibrit Yöntem Geliştirilmesi", Proje No: YBU-BAP-590, Araştırmacı, Ağustos 2013 - Ağustos 2015
Bu çalışmada, algoritma çalışma süresi kısa tutularak gürültü azaltma performansının geliştirilmesi için l0-norm, l1-norm ve l2-normun avantajları ve yerel olmayan ortalama filtrenin doku koruma özelliği bir araya getirilerek yeni bir yöntem geliştirilmektedir. Önerilen yöntem görüntüdeki kenar ve noktasal saçıcıların bozulmasını önleyerek homojen bölgelerin yumuşatılmasını sağlamaktadır. Bu alanda yapılan çalışmalar incelendiğinde l0-norm, l1-norm ve l2-normun değişik uygulama senaryolarında birbirlerine göre avantajları olduğu görülmektedir. Görüntülerdeki her bir piksel için bu normlardan uygun olanı kullanılırsa daha iyi bir gürültü azaltma sağlanacaktır. Ayrıca yerel olmayan ortalama filtrenin kullanımı ile de görüntü üzerindeki dokular daha iyi korunabilecektir.
Bu yöntemleri bir arada kullanabilmek için yöntemlerin sahip olacağı farklı ağırlık değerlerinden oluşan bir maliyet fonksiyonu tanımlanmaktadır. Önerilen maliyet fonksiyonunun eşlenik gradyan yöntemleri kullanılarak minimize edilmesiyle gürültü azaltma gerçekleştirilmektedir. Önerilen yöntem etkin bellek kullanımı sağlamaktadır ve yöntemin tüm adımlarının CPU’da OpenMP ve GPU’da CUDA kullanılarak paralelleştirilmesi sağlanmaktadır. Benek gürültü azaltma performansı, çalışma süresi ve bellek kullanımı sentetik ve gerçek SAR görüntüleri üzerinde test edilmiştir.

∴ KBÜ Lisans BAP Projeleri
∴ Tübitak 2241-Sanayi Odaklı Lisans Bitirme Projeleri
∴ Tübitak 2209-Üniversite Araştırma Projeleri
∴ Tübitak 2242-Üniversite Öğrencileri Araştırma Proje Yarışmaları
∴ İşitme Kaybı Teşhisinde Makine Öğrenimi Yöntemlerinin Uygulanması, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2024 (Proje Öğrencileri: Beyza KUZU)
∴ Histopatolojik Görüntülerden Derin Öğrenme Modelleriyle Kolon Kanserinin Teşhisi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2024 (Proje Öğrencileri: Betül SAMANCI)
∴ Denim Kumaşlarda Spektrofotometreden Elde Edilen Ölçüm Sonuçlarının Makine Öğrenmesi ile Kümelenmesi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2024 (Proje Öğrencileri: İrem SÖNMEZGÜL)
∴ Özellikleri Geliştirilmiş Evrişimli Sinir Ağları Kullanılarak Evre 1 Meme Kanseri Teşhisi ve Prognozunun Yapılması, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2023 (Proje Öğrencileri: Ebru KIRIKKAYIŞ)
∴ Mask R-CNN ile Özelleştirilmiş Sinir Ağları Kullanılarak Rahim Ağzı Kanseri Tür Ve Evre Tespiti, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2023 (Proje Öğrencileri: Beyza AKYILDIZ)
∴ Yaşlı Bakım Merkezlerinde Düşmeye Bağlı Oluşabilecek Yaralanmalar İçin Yenilikçi Tespit Sistemi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2023 (Proje Öğrencileri: Buse SARIÇAYIR, Esmanur ALİCAN)
∴ Ön Eğitimli Evrişimsel Yapay Sinir Ağları Kullanılarak Panaromik Görüntülerde Çürük Tespiti, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2022 (Proje Öğrencileri: Sinan Cem DAĞTEKİN, Atıf Aybars YALÇIN)
∴ İşitme Engellilerin Günlük Yaşamda İletişim Kurabilmesi için Mobil Uygulama, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2022 (Proje Öğrencileri: Resmiye Melisa TEMEL, Eren MUTLU, Erkay KARAKOÇ, Sinan Muharrem YILMAZ)
∴ Panoramik Diş Görüntülerinin Derin Öğrenme Yöntemleri ile Analizi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2021 (Proje Öğrencileri: Dilara ÖZDEMİR, Elif MEŞECİ, Süheda ÇİLEK)
∴ Yapay Zeka Destekli Otizmli Çocuk Egitmeni, Tübitak 2209 ve Tübitak 2242, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Mücahit Mustafa ÖKÇEN)
∴ Yüksek Frekanslı Kameralardan Gelen Görüntüler Üzerinde Çelik Hasar Tespiti, Tübitak 2209 ve Tübitak 2242, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Mihra YILDIZ)
∴ Yüz Şekillerine Göre Gözlük Öneren Uygulama, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Serap AYDOĞDU, Ece AKGÜL)
∴ Video Hakem Egitimi Uygulaması, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Emre SARAÇ, Ali Kemal ŞAHİN)
∴ Bir Hikaye Bırak, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Merve YILDIZ, Kadriye AKSAKAL)
∴ Konuşma Arkadaşım, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Caner KOYUN, İrem DEMİRÖZ)
∴ Görüntü Işleme ve Derin Ögrenme ile Görüntü Analizi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2020 (Proje Öğrencisi: Mert YILMAZ)
∴ Yüz Felci (Facial Paralysis) Hastalığını Tespit Eden Mobil Tabanlı Uygulama, Tübitak 2242, Proje Danışmanı, 2019 (Proje Öğrencisi: Buse Yaren TEKİN, Arzu YILDIZ)
∴ Engelli Çocuklarda Fizik Tedavi İçin Eğlenceli Hareket Sistemi, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2019 (Proje Öğrencisi: Pembe Buse KAYALI)
∴ MeTe: Metin Tercümanı (Doğal Dil İşleme Teknikleri ile Hikaye Kitaplarındaki Karakterlerin Duygu Analizi), Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2019 (Proje Öğrencisi: Çağatay AYDIN)
∴ WeWantEducation: Öğrenciler Arası Eğitim Ağının Mobil Uygulama İle Sağlanması, Karabük Üniversitesi Lisans Öğrencisi Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-17-LÖAP-127, 2017 (Proje Öğrencisi: Cahit Berkay KAZANGİRLER)
∴ SECUREYELLOW: Ticari Taksilerde Yüz Tanıma Sistemi İle Suçlu Analizi, Karabük Üniversitesi Lisans Öğrencisi Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-17-LÖAP-122, 2017 (Proje Öğrencileri: Sinem ERDOĞAN, Halil İbrahim ÇOPURKUYU)
∴ Makine Öğrenmesi ve Veri Madenciliği Yöntemleri ile Büyük Veri Analizi, Karabük Üniversitesi Lisans Öğrencisi Araştırma Projesi, Proje Yürütücüsü, Proje No: KBÜBAP-17-LÖAP-123, 2017 (Proje Öğrencisi: İskender Ülgen OĞUL)
∴ Maden Araç Takip Sistemi, Tübitak 2241, Proje Danışmanı, 2017 (Proje Öğrencileri: Semih CELAL, Muhammet Taha AYDIN)
∴ Görüntü İşleme ve Veri Madenciliği Yöntemleri Kullanılarak Görüntü Analizi (Gözcü++), Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2017 (Proje Öğrencileri: Mustafa BULUT, Sercan ÇOLAK)
∴ Renklerdeki Müzik, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2017 (Proje Öğrencileri: Kübra ÖZDEMİR, Mustafa Mert GÜN)
∴ Kanveren: Acil Kan İhtiyaci İçin Mobil Çözüm, Tübitak 2209, Proje Danışmanı, 2017 (Proje Öğrencileri: Onur AYDIN, Hasan AKGUL)

"Bilgisayar Kontrollü Ağaç Malzeme Yanma Düzeneği", Proje No: 110O548, Bursiyer, 2011 - 2013
Bu çalışmada amaç, bilgisayar kontrollü ağaç malzeme yanma düzeneği hazırlanarak yanma performansının bulanık mantık ile izlenmesidir. Bu sayede manuel ölçme ve insan kaynaklı hataların en aza indirilmesi, yanma sonucu elde edilen parametrelerin ve yanma sürecinin izlenmesi gerçekleştirilmektedir. Yanma esnasında yapılan ölçümlerin bilgisayar ortamına aktarılarak gerçek zamanlı olarak kaydedilmesi sağlanmaktadır. Yanma deneyi süresince ölçülen değerler üzerine bulanık çıkarım uygulanarak deneyin gerçek zamanlı performansı değerlendirilmekte ve yanma işlemi kontrol altında tutulmaktadır.
Yanma işlemi boyunca ve bitiminde elde edilen verilerin işlenmesi ve analizlerin yapılması yine bilgisayar ortamında gerçekleştirilmekte, elde edilen veriler tablo ve grafiklerle sunulmaktadır. Ölçüm sonucu kaydedilen tüm verilerin daha sonra yapılacak yanma çalışmalarında faydalanılmak üzere depolanması sağlanmaktadır. Bu sayede ileride yapılacak çalışmaların doğruluğu deneysel tecrübelerle kontrol edilebilecektir. Bu zamana kadar yapılan yanma çalışmaları bilgisayar kullanılmaksızın verilerin gözlemlerle okunması ve kaydedilmesi şeklindedir. Bu durum insan ve ölçme kaynaklı hataları beraberinde getirmektedir.
Bu çalışmada ise hataların tespit edilmesi ve deney performansının izlenmesi gerçek zamanlı olarak sağlanmaktadır. Hataların önceden tahmin edilmesi özellikle zaman ve iş gücünden tasarruf sağlamaktadır. Bu sayede düzenek, ağaç malzeme koruma teknolojisi ve ağaç malzemenin yanma özelliklerinin belirlenmesi alanında kullanılabilme özelliklerine sahip olmaktadır. Tarihi ahşap yapıların yanmaya karşı korunmasıyla ilgili yapılacak çalışmalara imkan tanınmaktadır. Tarihi ahşap evlerin yanma tehlikesine karşı korunabilmesi de tarihi kültürümüzün sürdürülebilirliğine katkı sağlayacaktır.
Yapmış olduğum akademik çalışmalara aşağıdaki listeden erişebilirsiniz.
Dental problems are one of the most common health problems for people. To detect and analyze these problems, dentists often use panoramic radiographs that show the entire mouth and have low radiation exposure and exposure time. Analyzing these radiographs is a lengthy and tedious process. Recent studies have ensured dental radiologists can perform the analyses faster with various artificial intelligence supports. In this study, the numbering performance of Mask R-CNN and our heuristic algorithm-based method was verified on panoramic dental radiographs according to the Federation Dentaire Internationale (FDI) system. Ground-truth labelling of images required for training the deep learning algorithm was performed by two dental radiologists using the web-based labelling software DentiAssist created by the first author. The dataset was created from 2702 anonymized panoramic radiographs. The dataset is divided into 1747, 484, and 471 images, which serve as training, validation, and test sets. The dataset was validated using the k-fold cross-validation method (k=5). A three-step heuristic algorithm was developed to improve the Mask R-CNN segmentation and numbering results. As far as we know, our study is the first in the literature to use a heuristic method in addition to traditional deep learning algorithms in detection, segmentation and numbering studies in panoramic radiography. The experimental results show that the mAp (@IOU = 0.5), precision, recall and f1 scores are 92.49%, 96.08%, 95.65% and 95.87%, respectively. The results of the learning-based algorithm were improved by more than 4%. In our research, we discovered that heuristic algorithms could improve the accuracy of deep learning-based algorithms. Our research will significantly reduce dental radiologists’ workload, speed up diagnostic processes, and improve the accuracy of deep learning systems.
Recently, it has become very popular to use electroencephalogram (EEG) signals in emotion recognition studies. But, EEG signals are much more complex than image and audio signals. There may be inconsistencies even in signals recorded from the same person. Therefore, EEG signals obtained from the human brain must be analyzed and processed accurately and consistently. In addition, traditional algorithms used to classify emotion ignore the neighborhood relationship and hierarchical order within the EEG signals. In this paper, a method including selection of suitable channels from EEG data, feature extraction by Welch power spectral density estimation of selected channels and enhanced capsule network-based classification model is presented. The most important innovation of the method is to adjust the architecture of the capsule network to adapt to the EEG signals. Thanks to the proposed method, 99.51% training and 98.21% test accuracy on positive, negative and neutral emotions were achieved in the Seed EEG dataset. The obtained results were also compared and evaluated with other state-of-the-art methods. Finally, the method was tested with Dreamer and Deap EEG datasets.
Bitewing radiographic imaging is an excellent diagnostic tool for detecting caries and restorations that are difficult to view in the mouth, particularly at the molar surfaces. Labeling radiological images by an expert is a labor-intensive, time-consuming, and meticulous process. A deep learning-based approach has been applied in this study so that experts can perform dental analyzes successfully, quickly, and efficiently. Computer-aided applications can now detect teeth and number classes in bitewing radiographic images automatically. In the deep learning-based approach of the study, the neural network has a structure that works according to regions. A region-based automatic segmentation system that segments each tooth using masks to help to assist analysis as given to lessen the effort of experts. To acquire precision and recall on a test dataset, Intersection Over Union value is determined by comparing the model's classified and ground-truth boxes. The chosen IOU value was set to 0.9 to allocate bounding boxes to the class scores. Mask R–CNN is a method that serves as instance segmentation and predicts a pixel-to-pixel segmentation mask when applied to each Region of Interest. The tooth numbering module uses the FDI notation, which is widely used by dentists, to classify and number dental items found as a result of segmentation. According to the experimental results were reached 100% precision and 97.49% mAP value. In the tooth numbering, were obtained 94.35% precision and 91.51% as an mAP value. The performance of the Mask R–CNN method used has been proven by comparing it with other state-of-the-art methods.
Today, thanks to the rapid development of technology, the importance of digital images is increasing. However, sensor errors that may occur during the acquisition, interruptions in the transmission of images and errors in storage cause noise that degrades data quality. Salt and pepper noise, a common impulse noise, is one of the most well-known types of noise in digital images. This noise negatively affects the detailed analysis of the image. It is very important that pixels affected by noise are restored without loss of image fine details, especially at high level of noise density. Although many filtering algorithms have been proposed to remove noise, the enhancement of images with high noise levels is still complex, not efficient or requires very long runtime. In this paper, we propose an effective denoising filter that can restore the image effectively in terms of quality and speed with less complexity for high density noise level. In the experimental studies, we compare the denoising results of the proposed method with other state-of-the-art methods and the proposed algorithm is quantitatively and visually comparable to these algorithms when the noise intensity is up to 90%.
Remote sensing and interpretation of hyperspectral images are becoming an increasingly important field of research. High dimensional hyperspectral images consist of hundreds of bands and reflect the properties of different materials. The need for more detail about objects and the improvement of sensor resolutions have resulted in the generation of higher size hyperspectral data. Many years of research have shown that there are many difficulties in the pre-processing of these data due to their high dimensionality. Recent studies have revealed that manifold learning techniques are a very important solution to this problem. However, as the complexity of the data increases, the performance of these methods cannot reach a sufficient level. This letter proposes a particle swarm-based multidimensional field embedding method inspired by the force field formulation to increase the performance. Detailed comparative analyses of the proposed method were made for Botswana and Kennedy Space Center (KSC) data. It is also shared in the results of other popular datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to existing manifold embedding methods in classification accuracy and visualization of hyperspectral data. In addition, an optimization-based solution is presented to the problem of parameter determination of existing embedding methods.
In this study, DentiAssist, a web-based radiological image analysis and labeling application supported by artificial intelligence, was developed for the education of dentistry students. The necessary legal permissions regarding the panoramic tooth images were obtained and ten students from the Faculty of Dentistry of Karabuk University were included in the study. In the AI-based analysis of the study, Mask R-CNN was used to detect and divide the teeth, providing information about the positions of the teeth in the region of interest and the pixels of the teeth. Using the labeling module of DentiAssist software, 649 training and 279 validation data, precisely labeled by three maxillofacial radiologists, were given as input into the neural network and a feature map was created with the convolutional neural network. At the pixel level, a mask was produced for each tooth and tooth detection was carried out with the Region of Interest Alignment module. Using an equal number of 100 test images, mAP (mean average precision) was measured 97.75% because of student and artificial intelligence comparison, and 99.02% success was achieved in radiologist and artificial intelligence comparison.
Classification of a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image is an essential process for SAR image analysis and interpretation. Recent advances in imaging technologies have allowed data sizes to grow, and a large number of applications in many areas have been generated. However, analysis of high-resolution SAR images, such in classification, is a time-consuming process and high speed algorithms are needed. In this study, classification of high speed denoised SAR image patches by using Apache Spark clustering framework is presented. Spark is preferred due to its powerful open source cluster-computing framework with fast, easy to use, and in-memory analytics. Classification of SAR images is realized on patch level by using the supervised learning algorithms embedded in the Spark machine learning library. The feature vectors used as the classifier input are obtained using gray-level co-occurrence matrix which is chosen to quantitatively evaluate textural parameters and representations. SAR image patches used to construct the feature vectors are first applied to the noise reduction algorithm to obtain a more accurate classification accuracy. Experimental studies were carried out using Naive Bayes, Decision Tree and Random Forest algorithms to provide comparative results, and significant accuracies were achieved. The results were also compared with a state-of-art deep learning method. TerraSAR-X images of high-resolution real-world SAR images were used as data.
Multidimensional field embedding methods have been demonstrated to effectively characterise spectral signatures in hyperspectral images. However, high-dimensional data composed of a number of classes presents challenges to the existing embedding methods. This Letter proposes an enhanced multidimensional field embedding algorithm based on the force field formulation. The comparative performance of the proposed algorithm is evaluated in the classification and visualisation of commonly used hyperspectral images. Experimental results demonstrate its superiority over previously used field embedding techniques.
Speckle noise inherent in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images seriously affects the result of various SAR image processing tasks such as edge detection and segmentation. Thus, speckle reduction is critical and is used as a preprocessing step for smoothing homogeneous regions while preserving features such as edges and point scatterers. Although state-of-the-art methods provide better despeckling compared with conventional methods, their resource consumption is higher. In this letter, a sparsity-driven total-variation (TV) approach employing l0-norm, fractional norm, or l1-norm to smooth homogeneous regions with minimal degradation in edges and point scatterers is proposed. Proposed method, sparsity-driven despeckling (SDD), is capable of using different norms controlled by a single parameter and provides better or similar despeckling compared with the state-of-the-art methods with shorter execution times. Despeckling performance and execution time of the SDD are shown using synthetic and real-world SAR images.
Günümüzde gittikçe önem kazanan uzaktan algılamada, araştırmacılar çeşitli spektral imzalar arasındaki ilişkileri bulmak için dünyanın yüzeyini temsil eden yüksek boyutlu verileri kullanırlar. Özellikle görüntüler, farklı malzemelerin özelliklerini yansıtan yüzlerce yüksek çözünürlüklü banttan oluşabilirler. Bununla birlikte, yüksek boyutlu uzayda çok sayıda farklı bantların bulunması, bu özelliklerin yorumlanmasını zorlaştırabilmektedir. Uzaktan algılama verilerinin ön-işlemesi için boyutsallık problemine bağlı olarak çeşitli zorluklar ile karşılaşılmaktadır. Bu alanda ortaya çıkan araştırmalar, bunun zor bir problem olduğunu ve tüm sorunlara tek bir çözüm olmadığını ortaya koymaktadır. Bununla birlikte, son çalışmalar katmanlı uzay öğrenme tekniklerinin hiperspektral görüntülerin ön işlemesinde çok önemli bir çözüm olduğunu göstermektedir. Bu çalışmada, en güncel katmanlı uzay yerleştirme yöntemlerinin hiperspektral veriler üzerindeki performansı karşılaştırmalı olarak analiz edilmiştir. Her bir yöntemin bu alanda en çok kullanılan iki farklı veri seti kullanılarak boyut indirgeme uygulaması gerçekleştirilmiş ve en yakın komşu (1NN) sınıflandırması ile performansı doğrulanmıştır. Elde edilen sonuçlara göre karşılaştırılan katmanlı uzay yerleştirme yöntemlerinin hiperspektral verilerin sınıflandırılmasında sınıf bazlı farklılıklar olsa da başarılı sonuçlar verdiği görülmektedir. Ayrıca her bir yöntemin çalışma zamanı grafik olarak sunulmuş ve hangi yöntemin daha hızlı çalıştığı sebepleriyle birlikte açıklanmıştır.
Demir cevherinden sıvı ham demir üretimi, yüksek fırın işletmesinde gerçekleşmektedir. Bu süreç, uzun ve karmaşık bir yapıya sahiptir. Bir dökümün tamamlanması, yüksek fırının üretim kapasitesine bağlı olarak, 6-8 saat sürmektedir. Bu çalışmada entegre demir-çelik fabrikasının yüksek fırınlarına ait hammadde verileri kullanılıp üretilen sıvı ham demir miktarı, yapay sinir ağları vasıtasıyla tahmin edilmesi amaçlanmıştır. Bu çalışmada yüksek fırının çalışma biçimi incelenerek giriş ve çıkış parametreleri belirlenmiştir. 2016 ve 2019 yıllarına ait 1000 adet üretim verisinin %70’i eğitim, geriye kalan %30’u test verisi olarak ayrılmıştır. Veriler ilk adımda normalize edilerek yapay sinir ağı için kullanılabilecek duruma getirilmiştir. Test sürecinin ardından elde edilen sonuçlar, denormalize edilmiştir. Diğer taraftan yüksek fırının üretim yapmadığı zaman dilimleri veri setinden çıkarılmıştır. Yapay sinir ağı mimarisi için ara katmanda bulunan nöron sayıları üzerinde denemeler yapılmış ve en yüksek test başarısına sahip mimari seçilmiştir. İlk adım olarak veri setinin %70’lik kısmı yapay sinir ağına sonuçları ile beraber gösterilerek eğitim süreci tamamlanmıştır. Ardından girdi parametreleri verilen %30’luk kısım için, sonuçlar gösterilmeden, yapay sinir ağından tahmin edilmesi beklenmiştir. Eğitim sürecinde yapay sinir ağında Levenberg Marquardt, Bayesian ve Broyden-Flecther-Golgfarb-Shanno olmak üzere üç farklı öğrenme algoritması kullanılmıştır. Matlab R2016a platformunun kullanıldığı çalışmada eğitim algoritmalarına ait test sonuçları karşılaştırılmış ve %94’lük test başarı oranı ile Levenberg Marquardt Algoritması en iyi test sonucuna ulaşmıştır. İleri yönlü geri yayılımlı yapının kullanıldığı yapay sinir ağında ortalama mutlak yüzde hata oranı %5,89 bulunmuştur. Son adımda, Matlab platformunda tasarlanan yapay sinir ağı Visual Studio platformuna alınmış ve tahmin sonuçları yine ortalama mutlak yüzde hata çerçevesinde karşılaştırılmıştır. Yapılan karşılaştırmada Matlab programının Visual Studio platformundan daha iyi performans gösterdiği tespit edilmiştir
In this study, surfaces of solid objects are coloured with Cropped Quad-Tree method utilizing GPU computing optimization. There are numerous methods used in solid object colouring. When the studies carried out in different fields are taken into consideration, it is seen that quad-tree method displays a prominent position in terms of speed and performance. Cropped quad-tree is obtained as a result of the developments seen with the frequent use of this method in the field of computer sciences. Two different versions of algorithm which operate recursively on CPU and at the same time which use GPU computing optimization are used in this study. Besides, OpenGL is used for graphics drawing process. Within the setting of the study, results are obtained via CPU and GPU’s, at first using Quad-Tree method and then Cropped Quad-Tree method. It is observed that GPU computing is obviously faster than CPU computing and Cropped Quad-Tree method produces rapid results compared to Quad-Tree method as a result of performance. GPU computing method boosted approximately performance by up to 20 times compared to only CPU usage; furthermore, cropped quad-tree method boosted approximately performance of algorithm by up to 25 times on average dependent on screen and object size.
---
---
---
---
---
Recognition and interpretation of human activities are very interesting and hot topics that are frequently studied in the field of computer vision. Especially with the advent and development of the Microsoft Kinect depth sensors, the expansion of the study field has gained momentum in the positive direction. Thanks to RGBD cameras, which also provide depth information in addition to the RGB image, researchers benefit from many advantages in terms of privacy, accuracy and precision. In this study, automatic segmentation of repeated 3D human activity is proposed. A public dataset containing the repeated action sequences are recorded using the RGBD camera. The action sequence in this dataset includes similar and different action information. In order to identify and label each action in sequence, it is necessary to perform the segmentation process. To be able to perform a successful segmentation process, the data must be pre-processed to remove noise. For this purpose, a total variation based noise removal method is used. Human action recognition and detailed error analysis can be performed through the segments derived from the output of this work.
- Computer-aided curve and surface design models are used to design surfaces that do not have a particular shape. Since these surfaces cannot be expressed by known mathematical functions, curve and surface modeling methods such as Bezier, B-Spline and Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline (NURBS) have been developed. In this study, an application is developed that allows the NURBS curve algorithm, which is used as a method in 3D modeling, to be computed using Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) with parallel processing capability and displayed on the LCD touch screen. The B-Spline basis function which NURBS based on are sampled mathematically. The parametric values used in the display of the NURBS curves and surfaces are presented on the LCD with user interaction. Parametric values such as control points, knot vector, and weight vector are separately sampled for curves and mathematical solutions are given. The NURBS curve for user-defined control points can be displayed in real time on the screen. In addition, an implementation of the NURBS algorithm in the Visual Studio platform was developed and obtained results were compared.
With today's developing technology, people's access to information and its production have reached a very fast level. These generated and obtained information are instantly created, entered into data systems and updated. Sources of streaming data can be transformed into valuable analysis results when they are handled with targeted methods. In this study, a text data field is determined to perform analysis on instantaneous generated data and Twitter, the richest platform for instant text data, is used. Twitter instantly generates a variety of data in large quantities and it presents it as open source using an API. A machine learning framework Apache Spark's stream analysis environment is used to analyze these resources. Situation analysis was performed using Support Vector Machine, Decision Trees and Logistic Regression algorithms presented under this environment. The results are presented in tables.
Image processing system, which is inspired by the vision of individuals, is now used in many sciences. Image processing which involves transferring and processing images to a computer using different methods and tools has resulted in the acquisition of a new image or interpretation of the current image. Image processing systems in the industry have also contributed to increased production requirements. At this point, the areas where image processing systems are used have been utilized with minimum cost and maximum efficiency principle. In this study, an automation system has been realized which classifies the fruits in the video images according to their dimensions in real-time with the EmguCV graphic library which is used as a method in image processing models. The filter models that form the basis of the EmguCV library are illustrated in this study. Mathematical solutions of the image processing are given separately for image smoothing and edge detection. Obtained results can be displayed in the application using OpenGL from net Framework classes. The application is built on Visual Studio 2012, OpenGL 3.0 and Windows 7 platforms.
Greenhouses provide the environmental conditions to be controlled and regulated as desired while allowing agricultural products to be produced without being affected by external environmental conditions. High quality and a wide variety of agricultural products can be produced throughout the year. In addition, mapping and detection of these areas has great importance in terms of factors such as yield analysis, natural resource management and environmental impact. Various remote sensing techniques are currently available for extraction of greenhouse areas. These techniques are based on the automatic detection and interpretation of objects on remotely sensed images. In this study, greenhouse areas were determined from optical images obtained from Landsat. The study was carried out in the greenhouse areas in Karabuk province. The obtained results are presented with figures and tables.
The increase in the number of devices and users online with the transition of Internet of Things (IoT), increases the amount of large data exponentially. Classification of ascending data, deletion of irrelevant data, and meaning extraction have reached vital importance in today's standards. Analysis can be done in various variations such as Classification of text on text data, analysis of spam, personality analysis. In this study, fast text classification was performed with machine learning on Apache Spark using the Naive Bayes method. Spark architecture uses a distributed in-memory data collection instead of a distributed data structure presented in Hadoop architecture to provide fast storage and analysis of data. Analyzes were made on the interpretation data of the Reddit which is open source social news site by using the Naive Bayes method. The results are presented in tables and graphs.
Speckle noise which is inherent to Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging makes it difficult to detect targets and recognize spatial patterns on earth. Thus, despeckling is critical and used as a preprocessing step for smoothing homogeneous regions while preserving features such as edges and point scatterers. In this study, a low-memory version of the previously proposed sparsity-driven despeckling (SDD) method is proposed. All steps of the method are parallelized using OpenMP on CPU and CUDA on GPU. Execution time and despeckling performance are shown using real-world SAR images.
Segmentation is widely used for determining tumor and other lesions and classifying tissues for various analysis purposes in medical images. However, being an ill-posed problem, there is no single segmentation method which can perform successfully for all kind of data. In this study, a novel total variation (TV) based skull segmentation method is proposed. Skull segmentation performance of the proposed method is shown using computed tomography (CT) images.
Speckle noise which is inherent to Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging obstructs various image exploitation tasks such as edge detection, segmentation, change detection, and target recognition. Therefore, speckle reduction is generally used as a first step which has to smooth out homogeneous regions while preserving edges and point scatterers. Traditional speckle reduction methods are fast and their memory consumption is insignificant. However, they are either good at smoothing homogeneous regions or preserving edges and point scatterers. State of the art despeckling methods are proposed to overcome this trade-off. However, they introduce another trade-off between denoising quality and resource consumption, thereby higher denoising quality requires higher computational load and/or memory consumption. In this paper, a local pixel-based total variation (TV) approach is proposed, which combines l2-norm and l1-norm in order to improve despeckling quality while keeping execution times reasonably short. Pixel-based approach allows efficient computation model with relatively low memory consumption. Their parallel implementations are also more efficient comparing to global TV approaches which generally require numerical solution of sparse linear systems. However, pixel-based approaches are trapped to local minima frequently hence despeckling quality is worse comparing to global TV approaches. Proposed method, namely mixed norm despeckling (MND), combines l2-norm and l1-norm in order to improve despeckling performance by alleviating local minima problem. All steps of the MND are parallelized using OpenMP on CPU and CUDA on GPU. Speckle reduction performance, execution time and memory consumption of the proposed method are shown using synthetic images and TerraSAR-X spot mode SAR images.
We propose an implementation for quad-tree based solid object coloring using Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA). There are numerous different techniques in use for solid object coloring. One commonly used technique is the quad-tree, which has evolved from work in different fields. A quad-tree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. The quad-tree somewhat follows the tree data structure commonly used in computer science. The normal tree data structure looks like an upside down tree, where a parent node at the top of the tree has one or more children nodes connected to it. The aim of this study is coloring of a solid object using screen splitting method. The screen is divided into squares via this method and whether one or more points of the object are available in the separated parts is searched. According to the existing points, algorithm is applied and the object coloring is provided by reducing pixel size. We implemented our algorithm using the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) computing and compared their performance with a CPU implementation. Nvidia CUDA library has been used for the GPU computing. CUDA gives developers access to the virtual instruction set and memory of the parallel computational elements in CUDA GPUs. We have tried our study on different systems that have different GPUs and CPUs. The computation studies were also evaluated for different solid objects. When we compared the results obtained from both systems, a better performance was obtained with GPU computing. According to results, GPU computation approximately worked 20 times faster than the CPU computation.
It is important to obtain the results of methods that are used in solving scientific and engineering problems rapidly for users and application developers. Parallel programming techniques have been developed alongside serial programming because the importance of performance has been increasing day by day while developing computer applications.Various methods such as Gauss Elimination (GE) Method, Gauss-Jordan Elimination (GJE) Method, Thomas Method, etc. have been used in solution of Linear Equation System (LES). In this study, performance comparison is done using Open Multi-Processing (OpenMP) and Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) for nxn matrix via GJE Method. GJE Method is a variant of GE which is used in solving linear system equations (Ax=B). Each step of GJE Method solution algorithm is independent from each other and also the method is appropriate for parallel computing structure; therefore, this method is preferred within the scope of this study. Application coded in C programming language is developed using OpenMP and CUDA. OpenMP is an Application Program Interface that allows parallel programming using compiler directives on Central Processing Unit (CPU). CUDA is known as NVIDIA’s parallel computing architecture add it enables significant increases in computing performance by the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).Application is realized on Intel Core 2 Quad CPU Q8200 2.33 GHz processor, GeForce 9500 GT graphic card. It is observed that application using Grid-Block-Thread structure and optimized with CUDA displays higher performance than OpenMP in terms of time.
In recent years, parallel processing has been widely used in the computer industry. Software developers, have to deal with parallel computing platforms and technologies to provide novel and rich experiences. We present a novel algorithm to solve dense linear systems using Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA). High-level linear algebra operations require intensive computation. In this study Graphics Processing Units (GPU) accelerated implementation of LU linear algebra routine is implemented. LU decomposition is a decomposition of the form A=LU where A is a square matrix. The main idea of the LU decomposition is to record the steps used in Gaussian elimination on A in the places where the zero is produced. L and U are lower and upper triangular matrices respectively. This means that L has only zeros above the diagonal and U has only zeros below the diagonal. We have worked to increase performance with proper data representation and reducing row operations on GPU. Because of the high arithmetic throughput of GPUs, initial results from experiments promised a bright future for GPU computing. It has been shown useful for scientific computations. GPUs have high memory bandwidth and more floating point units as compared to the CPU. We have tried our study on different systems that have different GPUs and CPUs. The computation studies were also evaluated for different linear systems. When we compared the results obtained from both systems, a better performance was obtained with GPU computing. According to results, GPU computation approximately worked 3 times faster than the CPU computation. Our implementation provides significant performance improvement so we can easily use it to solve dense linear system.
In this study, fuzzy logic graphical user interface software for evaluation of wooden material combustion performance is realized. The most accurate monitoring of measurements obtained by the combustion is provided. Operations on parameters that obtained from the result of combustion can be made faster. Test performance is determined with fuzzy logic by using data obtained during the combustion process and errors are reported to the user. Unexpected situations that experts could not notice can be determined easily by this software during the combustion. It has been observed that this user interface software prevents the data-loss and gives better results with sensitive measurements. Since repetition of the experiment is reduced, especially time, work and energy savings are provided. This fuzzy logic user interface software with these features can be used easily in wooden material combustion R&D centers, academic studies on this issue and companies in this area.
In this study, the real time control of DC-DC buck converter with fuzzy logic controller is presented. DC-DC converter circuit and real time Matlab/Simulink model that works with this circuit is prepared. For real time control, it is benefited from Real Time Windows Target library. Data acquisition card is used for data transfer between Simulink model and designed circuit. Fuzzy inference system prepared with FIS editor is embedded to fuzzy logic controller used in this model. The real time and non-real time simulations of fuzzy logic controller and PID comparisons are given with this study.
With the accumulation of technology from the recent years of development, the total amount of data that has been revealed daily at the point reached today are quite excessive in the last forty years. It is of vital importance in our day to clean, understand, classify and make a usable analysis report of this emerging data. Speed is a key factor for information retrieval in this important area. Apache Spark offers an innovative and robust solution to this problem. Unlike the previously used analysis methods, this solution stores data in the memory in order to gain speed in analysis, rather than performing data read/write operations through the disk during analysis. Spark provides near real-time speed with in-memory data read/write, analysis and resulting operations. In this study, a classification analysis was conducted on Reddit social entertainment site comments using Support Vector Machine (SVM) which is the supervised (educated) learning method. The results are presented in tables and graphics.
Speckle noise which is inherent to Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging obstructs various image exploitation tasks such as edge detection, segmentation, change detection, and target recognition. Speckle reduction is generally used as a first step which has to smooth out homogeneous regions while preserving edges and point scatterers. In remote sensing applications, efficiency of computational load and memory consumption of despeckling must be improved for SAR images. In this paper, an early-exit total variation approach is proposed and this approach combines the l1-norm and the l2-norm in order to improve despeckling quality while keeping execution times of algorithm reasonably short. Speckle reduction performance, execution time and memory consumption are shown using spot mode SAR images.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images contain high amount of speckle noise which causes edge detection, shape analysis, classification, segmentation, change detection and target recognition tasks become more difficult. To overcome such difficulties, smoothing of homogenous regions while preserving point scatterers and edges during speckle reduction is quite important. Besides, due to huge size of SAR images in remote sensing applications efficiency of computational load and memory consumption must be further improved. In this paper, a parallel computational approach is proposed for the Feature Preserving Despeckling (FPD) method which is chosen due to its success in speckle reduction. Speckle reduction performance, execution time and memory consumption of the proposed Fast FPD (FFPD) method is shown using spot mode SAR images.
Açık kaynak kodlu işletim sistemi, öğrenim yönetim sistemi ve sanal sınıf uygulaması ile gerçekleştirilen makul sayıda öğrencinin olduğu bir uzaktan eğitim altyapısında: hizmet kalitesini arttırmanın ve hizmet verilen öğrenci sayısını arttırarak bunu gerçekleştirmenin yolları irdelenmiştir. Çalışma özellikle sanal sınıf uygulamalarında performans artırımı ile ilgilenmektedir. Yeni, daha güçlü sunucular alarak başarım sağlamak her kurumsal yapıya uydurulamayacağından veya her kurum vizyonu yenilendiğinde ona uygun alt yapı değişikliği gerektirdiğinden, aşağıda da detaylandırıldığı üzere buna alternatif yöntem önerilmiş, modellenmiş ve gerçekleştirilmiştir.
Bilgisayar Mühendisliği, bilgisayar ve ilgili cihazların tasarımı, üretimi, işletimi ve bakımı ile ilgili mühendislik dalıdır. Donanım, yazılım, iletişim ve bunların arasındaki etkileşimleri inceler. Bilgisayar mühendisliği öğrencileri, teoriler, ilkeler, geleneksel elektrik mühendisliği pratikleri ve matematiğe odaklanır ve bunları bilgisayarlar ya da bilgisayar temelli sistemler tasarlama problemlerine uygular. Eğitimin ilk yıllarında matematik, fizik, kimya ve bilgisayar mühendisliğine giriş dersleri, daha sonraki yıllarda sistem programcılığı ve donanım kısmını oluşturan ve uzmanlaşmayı gerektiren dersler verilmektedir. Bilgisayar mühendisliğinde, programlama dilleri, veri yapıları, olasılık ve istatistik, sayısal mantık sistemleri, elektrik devreleri, temel elektronik, bilgisayar mimarisi, mikroişlemci ve mikro bilgisayar, sistem programlama, veri tabanı yönetim sistemi, bilgisayarlı grafik, işletim sistemi, yöneylem araştırma, formal diller ve soyut bilgiler, dil işleyiciler, bilgi sistemleri mühendisliği ile uygulamaya yönelik program yürütülmektedir. Lisans programımız, bilgisayar mühendisliğinde gerekli tüm temel bilgileri vermenin yanı sıra, profesyonel mühendislik için gerekli olan teknolojiyi yakından takip eden genç ve dinamik öğretim üyesi kadrosuyla kısa süre içerisinde gerçekleştirmeyi başarabilecek düzeydedir. Bölümümüze 2009-2010 eğitim-öğretim yılından itibaren normal öğretim ve ikinci öğretim olmak üzere 80 öğrenci alınacaktır. Bölümümüzde 2009-2010 yılından itibaren ülkemizde birkaç üniversitede uygulaması bulunan Uzaktan Eğitim Merkezi aracılığıyla uzaktan eğitimle Bilgisayar Mühendisliği Lisans programında bilgisayar mühendisi olma fırsatı sunulmaya başlanacaktır. 2008-2009 eğitim-öğretim yılından itibaren yüksek lisans ve doktora programları açılmış olup, mezun olacak öğrencilerimiz akademik çalışma yapabilme fırsatına sahiptirler.
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) image classification plays an important role in the analysis and interpretation of SAR images. In general, SAR image classification has a wide field of application in many areas. However, the analysis of high-resolution SAR images, such as classification, is a time-consuming process due to its size. In this study, SAR image patch classification is provided efficiently using Apache Spark framework. A successful classification was performed using the Naive Bayes method in the Spark MLlib library for image classification. Feature vectors required for each SAR image patch are obtained using gray-level cooccurrence matrix (GLCM).
In this paper, we present the implementation details and CPU/GPU parallelization of Sparsity Driven Despeckling (SDD) method which we proposed before. In this method, a sparsity driven total variation (TV) approach employing l0-norm, fractional norm, or l1-norm in order to smooth homogeneous regions with minimal degradation in edges and point scatterers is proposed. An observation image corrupted by speckle noise is taken into consideration and SAR image despeckling problem is defined as the optimization problem with minimization of the proposed cost function. In order to use convex optimization methods, corresponding cost function is approximated and written in a matrix-vector form. This matrix-vector form enables a special iterative optimization method where a linear system is solved in each step. Linear system which consists of positive definite symmetric matrix is solved efficiently using preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) iterative solver. PCG with IC preconditioner is implemented single threaded since construction of IC preconditioner, lower and upper Gaussian eliminations are not efficiently parallelizable. PCG with Jacobi preconditioner is parallelized using OpenMP on CPU and CUDA on GPU since all employed operations are efficiently parallelizable. All step of the preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm is also parallelized using OpenMP and CUDA. During the PCG algorithm, new strategies were developed to minimize the transfer from the CPU to the GPU. We used tiling approach for large images which PCG consumes too much memory. Therefore streams which have an ability to perform multiple CUDA operations simultaneously are used to run multiple tiles concurrently. Dynamic parallelism that enables a CUDA kernel to create and synchronize new nested work is designed. We realized our studies with two versions of the developed method using and not using dynamic parallelization. We performed our test studies with GeForce and Tesla GPUs and we also used Nvidia Jetson TK1 development kit for mobile platforms. In consequence, the results show that our method provides extremely fast (near-real-time) and high-quality SAR despeckling. All the alternative implementations of the SDD method are tested and information is given about cases in which ones could be chosen. Despeckling performance, execution time and memory consumption of the proposed method are shown with detailed tables and figures using synthetic images and real-world SAR images.
Aktif olarak girilen ve önceki yıllarda girilmiş olan dersler için bilgiler aşağıda verilmektedir.
2025/2026 YILI DERSLERİ TELEGRAM ANLIK İLETİŞİM GRUPLARI
- PROGRAMLAMA DİLLERİ TELEGRAM LİNKİBu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Ders Sunumları:
Hafta 1. Programlamaya Giriş (Introduction to Programming): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 2. Değişken Kavramı ve Temel Operatörler (Variable Concept and Basic Operators): İngilizce - Türkçe
Download Flowchart Diagram Software / Online: https://www.draw.io/
Hafta 3. Karar Yapıları (Decision Structures): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 4. Döngü Yapıları (Loop Structures): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 5. Akış Diyagramı Örnekleri (Examples and Analysis of Algorithms): İngilizce - Türkçe
Flowchart Examples 1 - Flowchart Examples 2
Download Additional Course Files
Hafta 6. Akış Diyagramı Örnekleri (Examples and Analysis of Algorithms): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 7. C Programlama Diline Giriş ve C Derleyicisi (Introduction to C Programming Language and C Compiler): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 8. C Dilinde Değişken Tipleri ve Temel Giriş/Çıkış İşlemleri (Variable Types in C Language and Basic Input/Output Operations): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 9. C Dilinde Kontrol ve Döngü Yapıları (Control and Loop Structures): İngilizce - Türkçe
Download Additional Course Material
Hafta 10. Diziler (Arrays): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 11. Çok Boyutlu Diziler (Multidimensional Arrays): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 12. Karakter Tutan Diziler (Character Array (String)): İngilizce - Türkçe
Download Additional Course Files
String Examples 1 - String Examples 2
String Examples 3 - String Examples 4
Hafta 13. Fonksiyonlar (Functions): İngilizce - Türkçe
EK DOKÜMANLAR:
C Programlamaya Giriş Video Serisi
Programlamaya Yeni Başlayanlar İçin Tavsiyeler ve Öğrenme Yolları
How to Start Learning Computer Programming
1. Algoritma ve Akış Diyagramı Örnekleri (Video Series)
3. Algorithms and Flowchart (Web)
4. Flowchart Examples: How a Flowchart Can Help You Program Better (Web)
Programlama Dilleri 1 Dönem Arası Çalışma Projeleri: Proje1 / Proje2
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Ders Sunumları:
Hafta 1. Sayısal Görüntü İşlemeye Giriş: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 2. Görüntünün Alınması ve Sayısallaştırılması: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 3. Görüntü İşleme ile İlgili Temel Kavramlar: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 4. Yoğunluk Dönüşümleri ve Histogram İşlemer: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 5. Uzamsal Filtreleme: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 6. Görüntü Onarma ve Geriçatma: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 7. Renkli Görüntü İşleme 1: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 8. Renkli Görüntü İşleme 2: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 9. Morfolojik Görüntü İşleme: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 10. Görüntü Sıkıştırma: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 11. Görüntü Bölütleme: İngilizce - Türkçe
Ek Kaynaklar:
Intro to Digital Image Processing: Online Course
E-book: Image Processing in C: Link
OpenCV 2.4 Cheat Sheet (C++): Link
E-book: Learning OpenCV: Link
Dijital Görüntü ve Video İşlemenin Temelleri: Online Course
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Ders Sunumları:
Hafta 1. Kapsama Kuralları ve Rasgele Sayı Üretimi (Scope Rules and Generating Random Numbers): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 2. C Bellek Düzeni ve Rekürsif Fonksiyonlar (Memory Layout of C and Recursive Functions): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 3. Rekürsif Fonksiyon Örnekleri (Recursive Function Examples): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 4. İşaretçiler (Pointers): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 5. İşaretçiler 2(Pointers 2): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 6. İşaretçiler 3(Pointers 3): İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 7. String Functions: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 8. Enum, Typedef, Struct: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 9. Linked Lists:İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 10. Sequential Access Files: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 11. Random Access Files: İngilizce - Türkçe
Hafta 12. Bitwise Operations İngilizce - Türkçe
Konu Videoları:
Passing Parameters to Functions (Animation)
Passing Arrays to Functions (Animation)
Recursive Computation of Factorial (Animation)
Recursive Computation of Factorial (Animation)
Dynamic Memory Allocation 1 (Animation)
Dynamic Memory Allocation 2 (Animation)
Ek Dokümanlar (Yeniden Eskiye Doğru)
C Programming Examples using Recursion
POINTERS:
2. C Programlama Dersleri (Pointers: Ders 33-36) (Video)
3. Pointer (computer programming) (Web)
5. A Tutorial on Pointers and Arrays in C (Web)
6. The Basics of C Programming (Web)
7. Pointers in C/C++ (Video Series)
LINKED LIST:
Linked List Video Series (1-10)
FILE OPERATIONS:
Kolay C Alıştırma (Dat Dosyasına Struct Dizisi Yazdırma)
Kolay C Alıştırma (Txt Veritabanlı Telefon Rehberi-Kayıt Ekleme)
Sıralı Erişimli Dosyalar (C'de Dosya İşlemleri)
Kolay C Programlama Dersleri: 1) Dosya İşlemleri-Giriş
Kolay C Programlama Dersleri: 2) Dosyaya Veri Yazma
Kolay C Programlama Dersleri: 3) Txt Dosyasından Veri Okuma
C Programlama: 1) Dosya İşlemlerine Giriş
C Programlama: 2) Dosyaya Bilgi Kaydetme
C Programlama: 3) Dosyadan Bilgi Okuma
BITWISE:
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere makine öğrenme kavramını ve farklı öğrenme metodlarını öğretmektir. Makine öğrenmesi algoritmalarının hem teorik bilgilerini hem de pratik olarak gerçek veriler üzerinde uygulaması sağlanacaktır. Öğrenciler, yöntemlerin hata ve karmaşıklık açısından nasıl analiz edeceğini öğrenecektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere makine öğrenme kavramını ve farklı öğrenme metodlarını öğretmektir. Makine öğrenmesi algoritmalarının hem teorik bilgilerini hem de pratik olarak gerçek veriler üzerinde uygulaması sağlanacaktır. Öğrenciler, yöntemlerin hata ve karmaşıklık açısından nasıl analiz edeceğini öğrenecektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere makine öğrenme kavramını ve farklı öğrenme metodlarını öğretmektir. Makine öğrenmesi algoritmalarının hem teorik bilgilerini hem de pratik olarak gerçek veriler üzerinde uygulaması sağlanacaktır. Öğrenciler, yöntemlerin hata ve karmaşıklık açısından nasıl analiz edeceğini öğrenecektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere bilimsel araştırma ve inceleme tekniklerinin öğretilmesi, elde ettikleri verilerin kullanılmasını ve sunulmasının öğretilmesi.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere bilimsel araştırma ve inceleme tekniklerinin öğretilmesi, elde ettikleri verilerin kullanılmasını ve sunulmasının öğretilmesi.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere bilimsel araştırma ve inceleme tekniklerinin öğretilmesi, elde ettikleri verilerin kullanılmasını ve sunulmasının öğretilmesi.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere bilimsel araştırma ve inceleme tekniklerinin öğretilmesi, elde ettikleri verilerin kullanılmasını ve sunulmasının öğretilmesi.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
Bu dersin amacı, öğrencilere bilimsel araştırma ve inceleme tekniklerinin öğretilmesi, elde ettikleri verilerin kullanılmasını ve sunulmasının öğretilmesi.
Bu dersin amacı, görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel ve ileri düzey işlemleri öğrenmek ve uygulayabilmek. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, problem çözümüne yönelik algoritma tasarlama ve C programlama dili kullanarak program geliştirmenin öğrenilmesi. C programlama tekniklerini kullanarak çeşitli problemlere çözüm bulunması.
Bu dersin amacı görüntü işlemede kullanılan temel prensipler ve algoritmaları öğrencilere öğretmektir. Öğrencilerin, bu ders sayesinde görüntü analizi işlemlerini gerçekleştirebilmeleri ve elde edilen sonuçları tartışabilmeleri amaçlanmaktadır.
Bu dersin amacı, uzaktan algılamanın temel kavramları ile uydu görüntülerinin işlenmesi, yorumlanması ve analizi işlemlerini öğrencilere öğretmektir.
Bu dersin amacı, işaretçiler ve listelerin kullanımını anlamak. Basit sıralama ve arama algoritmalarını öğrenmek. Öğrencilerin dosya işlemleri, bitişlemler, görsel programlama ve temel grafik işlemleriyle etkin programlar yazmasını sağlamaktır.
The purpose of this course is to get students to gain the ability of modelling standard and data-based technology. Turning the database of Entity-Relation or Object-Role into relational modelling.
The purpose of this course is to teach data structures with C programming language in details.
Introducing the most important high-level file structures tools which include indexing, co-sequential processing, B trees, Hashing.
Dersin amacı gerçek hayat problemlerinden hareketle, farklı alanlarda kullanılabilecek algoritmaların sunulmasıdır.
Bu dersin amacı öğrencilere C programlama dilinde işaretçi (pointer) kullanımı, bit düzeyinde işlem yapma, dosya işlemleri, sıralama algoritmaları, görsel programlama konularında yetenek kazandırmaktır.
Bu ders öğrencilere C programlama dilini kullanarak yapısal programlamanın temel kavramlarını öğretir.
2025/2026 GÜZ DÖNEMİ DERSLERİ TELEGRAM ANLIK İLETİŞİM GRUPLARI
- PROGRAMLAMA DİLLERİ TELEGRAM LİNKİGÜZ DÖNEMİ DUYURUSU:
2025/2026 Güz Döneminde Tüm Öğrencilerimize Başarılar Dilerim..
DERS DEVAM YÖNERGESİ:
MADDE 23–(1) Dönem içerisinde derse ve uygulamalara devam zorunludur. Teorik derslerin %30’undan, uygulamalı derslerin %20’sinden fazlasına katılmayan öğrenci o dersin sınavlarına giremez.
YÜKSEKÖĞRETİM KURUMLARI ÖĞRENCİ DİSİPLİN YÖNETMELİĞİ:
MADDE 5 - (1) Kınama cezasını gerektiren eylemler şunlardır;
d) Sınavlarda kopyaya teşebbüs etmek.
MADDE 7 - (1) Yükseköğretim kurumundan bir yarıyıl için uzaklaştırma cezasını gerektiren eylemler şunlardır;
e) Sınavlarda kopya çekmek veya çektirmek,
MADDE 8 - (1) Yükseköğretim kurumundan iki yarıyıl için uzaklaştırma cezasını gerektiren eylemler şunlardır;
d) Sınavlarda tehditle kopya çekmek, kopya çeken öğrencilerin sınav salonundan çıkarılmasına engel olmak, kendi yerine başkasını sınava sokmak veya başkasının yerine sınava girmek,
BİTİRME PROJESİ ÖNERİ FORMU:
Öneri formlarını doldurduktan sonra word formatında "canerozcan@karabuk.edu.tr" mail adresine gönderiniz. Öneri formunu indirmek için tıklayınız.